Driving is a skill that involves constant vigilance, and even the most experienced drivers can miss crucial details in their peripheral vision due to a phenomenon called the blind spot. This article delves into the importance of Blind Spot Monitoring Systems (BSMS), a sophisticated technology designed to counteract this persistent driving hazard. BSMS is essential in enhancing driving safety by providing an extra set of eyes on the road.
Definition and Overview of Blind Spot Monitoring Systems
A Blind Spot Monitoring system, also known as a Blind Spot Information System, is an advanced safety technology designed to alert drivers about vehicles in their blind spots. Initially utilized in high-end luxury vehicles, these systems have become increasingly prevalent in all types of cars due to their effectiveness in promoting safety.
The principle underlying the Blind Spot Monitoring system is straightforward. It continuously monitors the vehicle’s surrounding areas, including both sides and the rear, which are not easily visible to the driver. By utilizing sensors, cameras, and radar, the system can detect when a pedestrian, cyclist, or another vehicle enters these hazardous areas, alerting the driver to the possibility of an accident.
Different car models and brands use varied methods to inform drivers. Warning lights near wing mirrors may flash, or an audio alert may sound. Some systems may vibrate the steering wheel or driver’s seat to provide tactile cues. Advanced techniques can also provide active support, such as automatically braking or steering if the driver does not respond to the alerts.
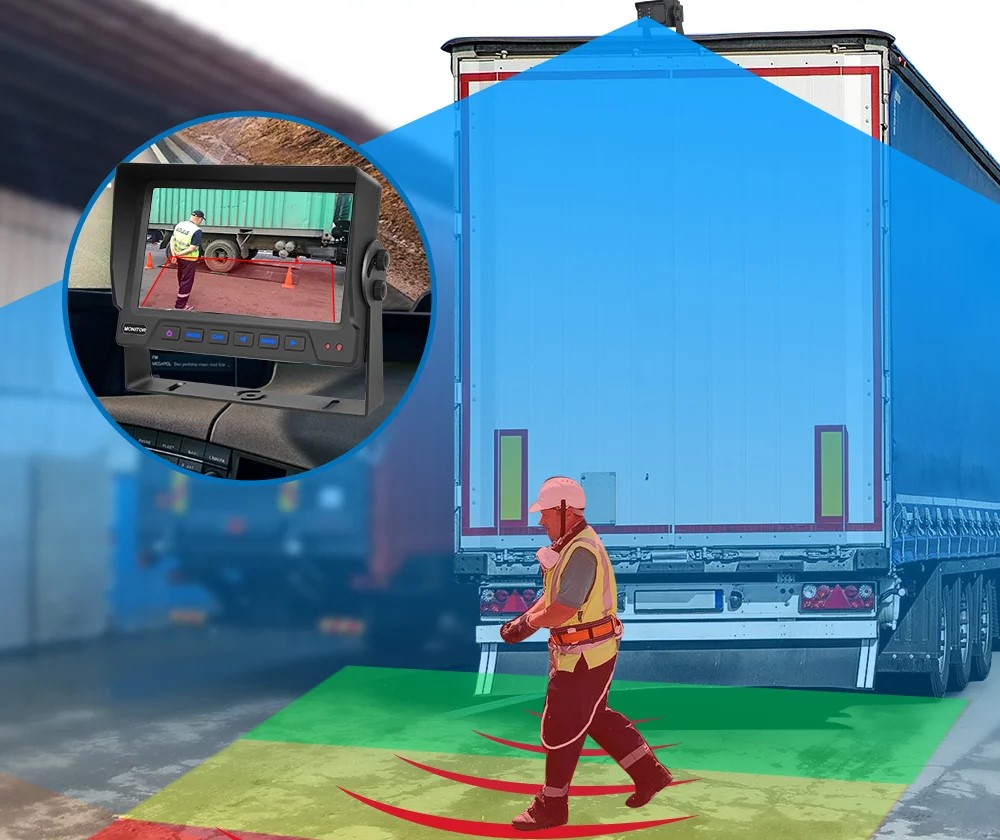

Blind Spot Monitoring systems are beneficial on highways or during parking when drivers need to change lanes, exit, or merge traffic safely and when vehicles are closely surrounding them. Experts believe blind spot-related crashes contribute to numerous accidents yearly, making these systems crucial to enhancing driving safety.
It’s crucial to note that Blind Spot Monitoring systems are not a substitute for driver attentiveness and the proper use of side and rearview mirrors. The purpose of these systems is to improve the efficiency of manual precautions. Adverse weather conditions or direct sunlight can sometimes affect the system’s efficacy, so drivers should rely on more than just such technologies.
In conclusion, Blind Spot Monitoring systems significantly advance vehicular safety technology. With continuous technological developments, these systems are expected to become even more precise in their detection capabilities, ensuring increased safety for drivers and all road users.
Benefits of Blind Spot Monitoring Systems
Blind Spot Monitoring Systems (BSMS) significantly increase the safety of the driver, passengers, and other road users. They help drivers identify obstacles or vehicles in their blind spot, notifying them to prevent possible collisions, especially during lane changes.
These monitoring systems breed confidence in drivers by giving them a better awareness of their surroundings. It reduces the stress of checking for blind spots, particularly in heavy traffic, further enhancing the driving experience.
Drivers often struggle with small-sized or improperly adjusted wing mirrors, which create substantial blind spots. With a blind spot monitoring system, drivers can substantially improve their visibility without constantly changing their mirrors.
Blind spot monitors provide immediate alerts, allowing drivers to make quick safety decisions. It improves road efficiency as drivers can change lanes or merge more confidently.
Blind spot detection systems have been proven to significantly reduce the occurrence of all lane-change crashes by 14%. Additionally, these systems are effective in preventing injuries resulting from such collisions, with a reduction of 23% (Source: Insurance Institute for Highway Safety – IIHS).
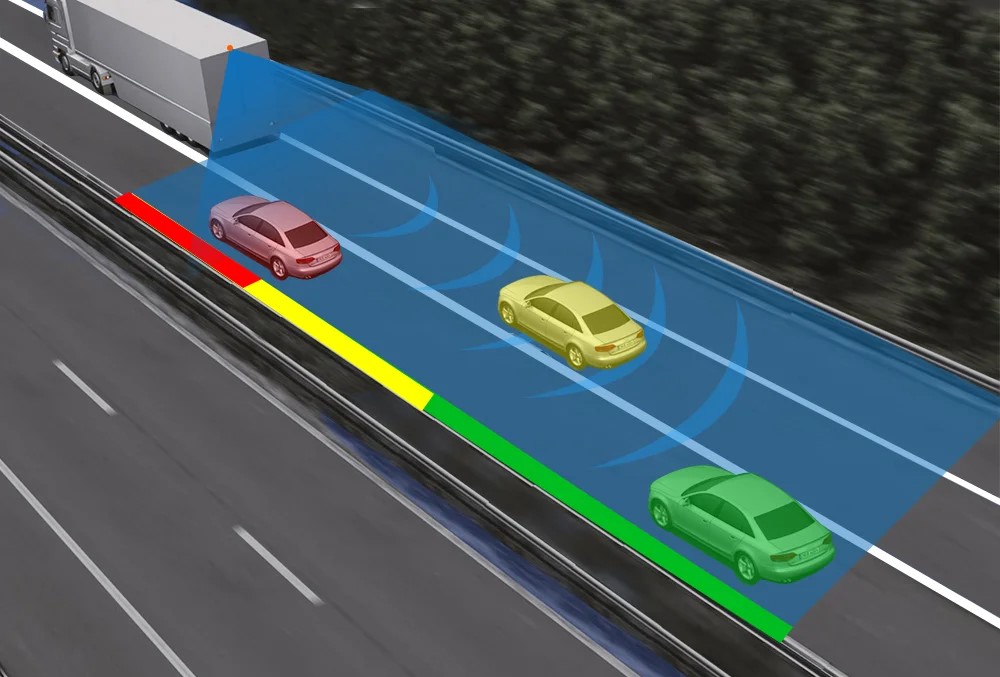
Most blind spot monitoring systems are intuitive and easy to use, providing audio, visual, or haptic warnings that even novice drivers can understand and act upon.
Some blind spot monitors also help in safe parking, especially in spots tight for side space. The system alerts drivers of approaching vehicles or obstacles that might not be visible through the mirrors alone.
The blind spot monitoring system is also beneficial in different driving conditions and situations, such as night driving, unfavorable weather conditions, highways, and heavy traffic, enhancing its overall usability.
While an upfront cost might be associated with installing a blind spot monitoring system, it can save drivers substantial amounts in the long run by preventing accidents involving repair costs.
By reminding drivers of where they need to check before making moves, these systems can promote safe driving habits, reducing overall road risks.
How Blind Spot Monitoring Systems Work
Blind Spot Monitoring Systems, also known as Blind Spot Detection or Blind Spot Information systems, consist of vehicle-based sensors that detect objects in areas around the vehicle that are not easily visible to the driver. These blind spots typically exist outside the driver’s peripheral vision or the vehicle’s mirrors.
The sensors used in Blind Spot Monitoring Systems are often located in the vehicle’s rear bumpers or door mirrors. Some vehicles also utilize cameras installed on the sides. The choice of sensor depends on the manufacturer and vehicle model.
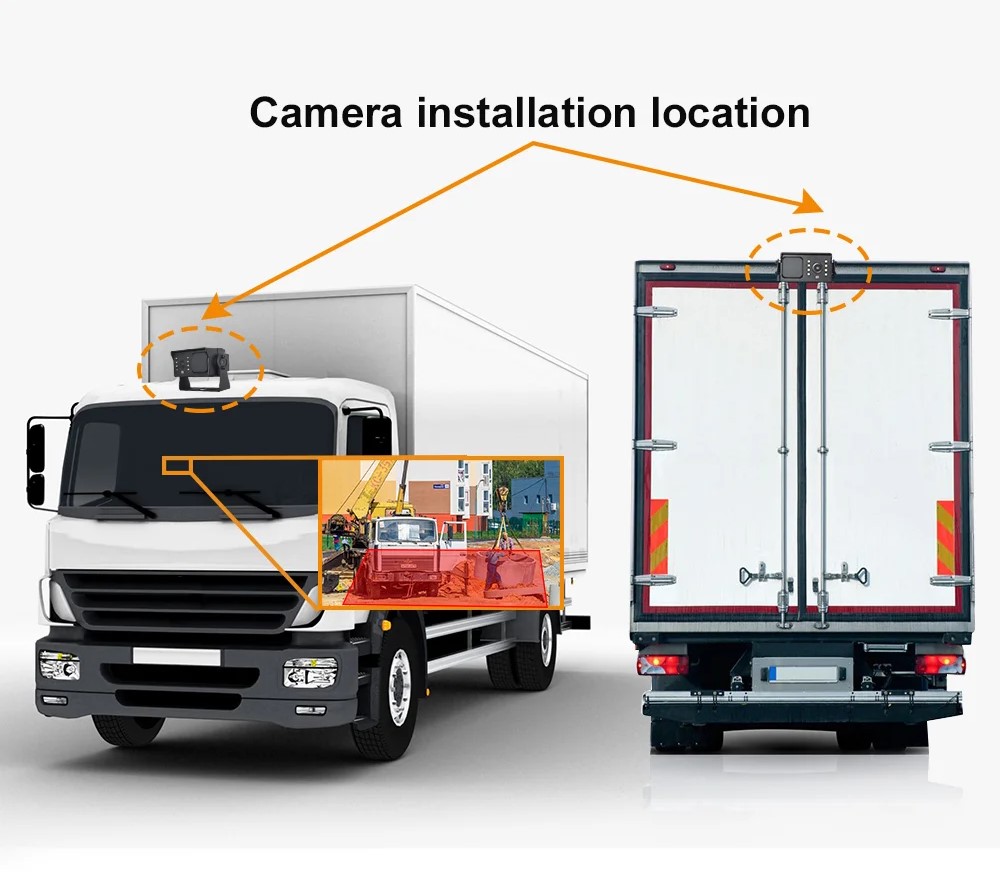
Most Blind Spot Monitoring Systems use radar sensors, although some may employ cameras or ultrasonic sensors. These sensors detect the presence of another vehicle or object when it enters the blind spot area. Radar sensors emit high-frequency electromagnetic waves that bounce off nearby objects. The system calculates distance by measuring the time it takes for waves to return.
When an object is detected in the blind spot, the driver is alerted through a light indicator on the corresponding side mirror and an audible warning sound.Advanced techniques may even provide tactile warnings, such as vibrations in the seat or steering wheel.
Specific advanced Blind Spot Monitoring Systems include additional features, such as Blind Spot Intervention. This feature, found in select high-end cars, actively manipulates the vehicle controls to prevent the driver from changing lanes if a vehicle is in the blind spot.
However, it is essential to note that Blind Spot Monitoring Systems have limitations. They may not detect objects in certain conditions, such as when the sensor is obstructed or when the thing is not within the sensor’s range. Drivers should always rely on their visual checks and use mirrors to ensure safety when changing lanes or making turns.
Statistics on the Effectiveness of Blind Spot Monitoring Systems
After thorough research, several statistics highlight the effectiveness of blind spot monitoring systems in enhancing driving safety. According to a study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), blind spot detection can reduce the risk of lane-change crashes by 14% and the risk of lane-change crashes with injuries by 23%. This significant decrease underscores the effectiveness of these systems in reducing accidents.
Furthermore, if all vehicles were equipped with blind spot detection, nearly 50,000 crashes could be averted each year in the US, preventing about 16,000 related injuries, according to another research from the IIHS.
Additionally, blind spot detection led to a 14% reduction in insurance claims for damage to other vehicles and an 11% reduction in shares for injuries to people in other cars, according to a report by the Highway Loss Data Institute (HLDI).
Vehicles equipped with blind spot detection systems were also found to have improved safety ratings, as reported by Consumer Reports. Moreover, nearly 80% of drivers using blind spot detection found the helpful technology, signifying its effectiveness in enhancing driving safety, according to research published in the Journal of Safety Research.
The utility of blind spot detection is further supported by the fact that 80% of drivers in a study by the US Department of Transportation deemed it very/somewhat helpful for judging whether it is safe to change lanes. Additionally, a survey by Autotrader revealed that 61% of people desired blind spot detection as a feature in their next vehicle.

OEM pre-installation statistics show that approximately 40% of all new cars sold in Canada in 2018 came with blind spot alerts, according to Statista. Moreover, AAA reported that drivers who initially didn’t trust blind spot monitoring systems gained trust in the technology after using it, with 80% having a positive perception of the system.
Drivers also perceive blind spot detection to enhance their safety, particularly in congested driving conditions. A study titled Naturalistic driving study: Descriptive analysis of light vehicle–heavy vehicle interactions in work zones” found that nearly two-thirds of participants agreed that their feeling of safety increased when using the system.
Limitations and Considerations of Blind Spot Monitoring Systems
While blind spot monitoring (BSM) systems are undoubtedly advantageous for driver safety, it is essential to recognize their limitations and considerations. Here are some key points to bear in mind:
1. False Alerts: Occasionally, BSM systems may trigger false alerts due to poor weather conditions, driving over uneven terrain at high speeds, or misinterpreting nearby objects such as fences or posts. Consequently, drivers may lose faith in the system or become overly dependent on it.
2. Limited Scope: BSM systems only cover blind spots in adjacent lanes and do not encompass areas nearer or further away from the vehicle. Consequently, drivers must manually check to ensure all blind spots are accounted for.
3. Delayed Alerts: In some cases, BSM systems may provide delayed alerts, particularly if a vehicle rapidly moves into the blind spot. This delay could lead to accidents.
4. Proper Installation: The effectiveness of a BSM system heavily relies on correct installation. If sensors are positioned incorrectly, efficiency and accuracy may be compromised.
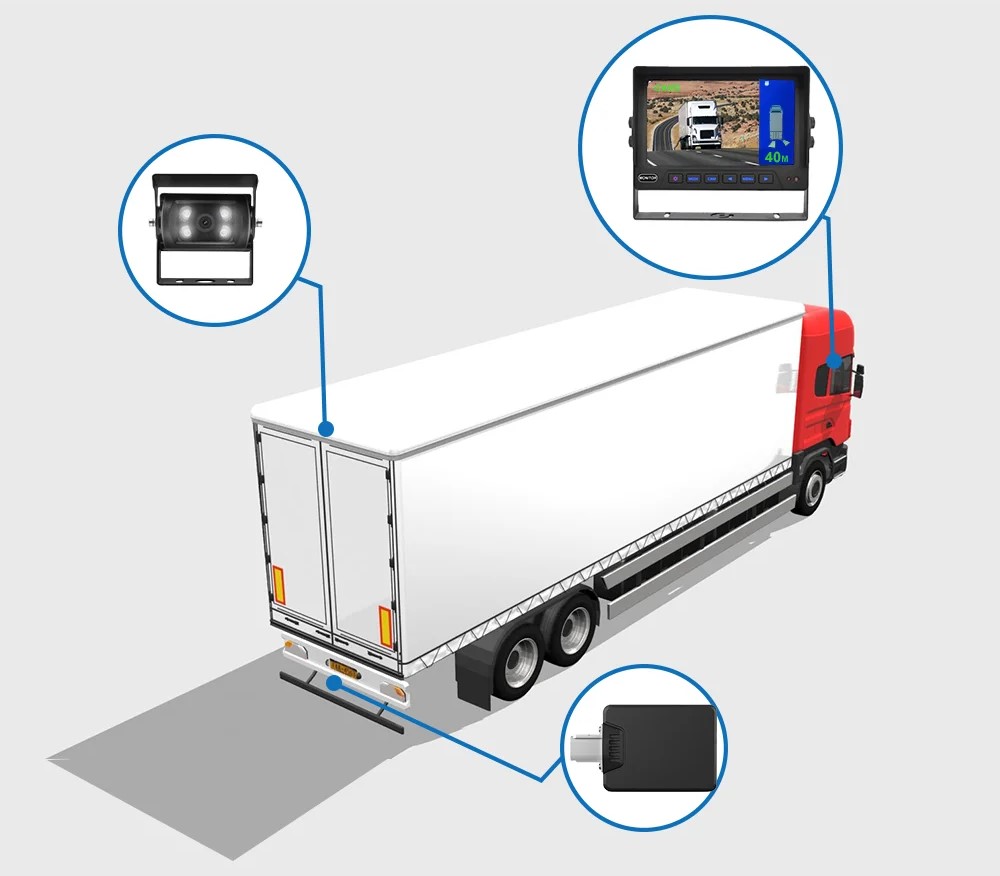
5. Sensor Limitations: Sensors used in BSM systems could be more flawless and can help detect smaller objects like bikes due to their size and speed. Additionally, sensors may not perform accurately during specific conditions like heavy rain, fog, or snow.
6. BSM systems are not intended to replace the need for manual blind spot checks but rather to serve as aids to enhance safety. Drivers should not solely rely on these systems.
7. Curb Detection: Most BSM systems fail to detect curbs, leaving vehicles vulnerable to scratches or dents in case of improper parking.
8. Calibration: BSM systems require periodic calibration to ensure their effectiveness. With regular check-ups, the system may provide correct readings.
9. Technology Malfunctions: Like all electronic systems, BSM can experience technical issues and malfunctions, compromising reliability.
10. Expense: Integrating a BSM system into a vehicle or selecting one during purchase incurs additional costs. Although many consider it a worthwhile investment for safety, it may only be affordable for some.
11. Maintenance: BSM systems necessitate regular maintenance to function correctly. This may involve sensor cleaning or routine electronics checks, contributing to the overall cost of vehicle maintenance.
12. Dependence: Over-reliance on BSM can breed complacency among drivers, leading them to neglect to check their blind spots thoroughly as they place excessive trust in the system.
By considering these points, one can attain a balanced perspective on the use of BSM in enhancing driving safety.
Throughout this article, we’ve detailed the impact of Blind Spot Monitoring Systems on driving safety, demonstrating how they help eliminate the dangerous blind spot issue many drivers face. The stark reduction in accidents due to employing BSMS is a clear testament to their vital role. Yet, it’s essential to consider that these systems are not infallible and require mindful usage to maximize their effectiveness.